Learning Playwright , web and cloudfare
Web
The current web page is advanced , the DOM is loaded only for the visible section on the page and the visible section can be increased or decreased based on the viewport height and width of the page ..
To load the DOM in natural way you will need to scroll it down to get to the next set of links and it builds the DOM tree and the tree !!
In google, the top level links are in <h3>
End to end automation using playwright
test files start with test_ like : test_example.py
Go to link : page.goto(‘https://playwright.dev’)
Extract title : expect(page).to_have_title(re.compile(“Playwright”))
Find a link with the name and click it = page.get_by_role(“link” , name=”Get Started”).click()
Expect page to have a heading with the name of Installation :
Almost everything starts with going to a page:
Goto : page.goto(url)
Interactions For interactions, we need to locate the elements. Playwright auto waits for elements to be actionable prior to performing the action.
locater_made = page.get_by_role(“link”, name=”Get Started”) # hover locater_made.click()
Radio element check : create a locator using page.get_by_role(“checkbox”).check()
Hover element : locator.hover()
Fill : locator.fill(“Name”) , here locator should be able to take some input
Press Key : locator.press(“
Assertions: expect(locator).to_be_checked(), checkbox is checked
## Before assertion :
<input type="checkbox" id="newsletter" />
<label for="newsletter">Subscribe to newsletter</label>
## After assertion :
<input type="checkbox" id="newsletter" checked />
<label for="newsletter">Subscribe to newsletter</label>
Actions
Interaction with HTML input elements using fill()
Text input
await page.get_by_role(“textbox”).fill(“Peter”) => locator.fill(“
Typing the characters sequentially in a input field:
Press keys one by one
await page.locator(‘#area’).press_sequentially(‘Hello World!’)
Press the keyboard keys :
await page.get_by_text("Submit").press("Enter") , press the enter button
await page.get_by_role("textbox").press("Control+ArrowRight")
Mouse down and Mouse up
await page.locator().hover()
await page.mouse.down() : keep the button pressed
await page.mouse.up() : release the button
one down() + one up() : means that a single click happened
Go to the last, forcing “infinite list” to load more content await page.get_by_text(“Footer text”).scroll_into_view_if_needed()
ScreenShot
screenshot an element matching the locator ...
await page.get_by_role("link").screenshot(animations="disabled", path="link.png")
animation : disable,
path : path_to_store_image
bounding box
Creates a bounding box of the element matching the locator !
box = await page.get_by_role("button").bounding_box()
await page.mouse.click(box["x"] + box["width"] / 2, box["y"] + box["height"] / 2)
Browser:
Playwright requires specific version of browser binaries to operate , using playwright CLI You can use any chromium browser that so a good choice would be to use brave browser .. You can run a script as soon as browser launches, that can be done by adding Init scripts to it … launch an extension in browser : https://playwright.dev/python/docs/chrome-extensions
Extension in browser: You can add extensions in browser to disable popup / cache / logins etc ..
using brave browser also gives this cloudfare fuckups , need to find something that bypass it
Learning Cloudfare
How does web works ?
WITHOUT CLOUDFARE
- The user contacts the DNS server of the website’s hosting provider, and asks for the IP of example.com
- The DNS server responds with the IP of the web server hosting example.com (e.g., 93.184.216.34)
- The user makes an HTTP request to that web server
- The web server responds with the web page
WITH CLOUDFARE
- Goes to its domain registrar, and sets the DNS servers to Cloudflare’s (e.g., kim.ns.cloudflare.com)
- sets up its Cloudflare account to work with the domain name (e.g., mycompany.com).
So when request is made for mycompany.com
-
The user contacts the DNS server kim.ns.cloudflare.com, and asks for the IP of mycompany.com
-
The DNS server responds with the IP of an intermediary Cloudflare server (e.g., 104.16.109.208)
-
The user makes an HTTP request to this server
-
Cloudflare checks the legitimacy of the request (presence of malicious-looking content, source IP address, in addition to other factors), and decides whether to let the request pass through or block it
-
If Cloudflare chooses to allow the request to pass through, it forwards it to the real web server responsible for mycompany.com (e.g., 188.226.197.73). This server is commonly called the origin server.
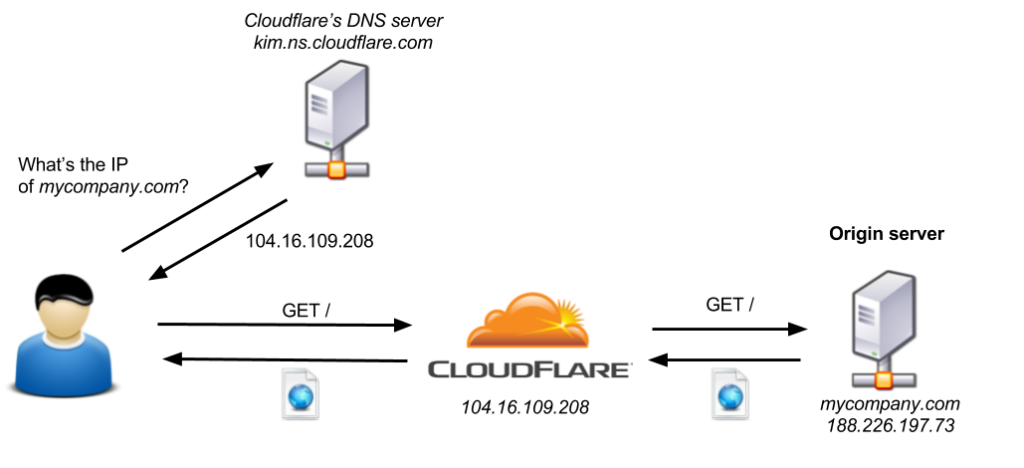
- For this protection to work, an attacker must not be able to access the origin server directly. Otherwise, it can just contact the origin server without passing through Cloudflare, and bypass any protection.
To sum up – a publicly accessible origin server is safe… as long as nobody finds its IP addresses.
Finding exposed origin servers / IP address is easy. Shodan and Censys scan the internet and make there data accessible for free ..
From this you will get IP of all hosted servers, and from there you can check if the IP is the one that is coming from cloudfare or from the origin server
What cloudfare does ?
